- Cancer Information
- Support & Services
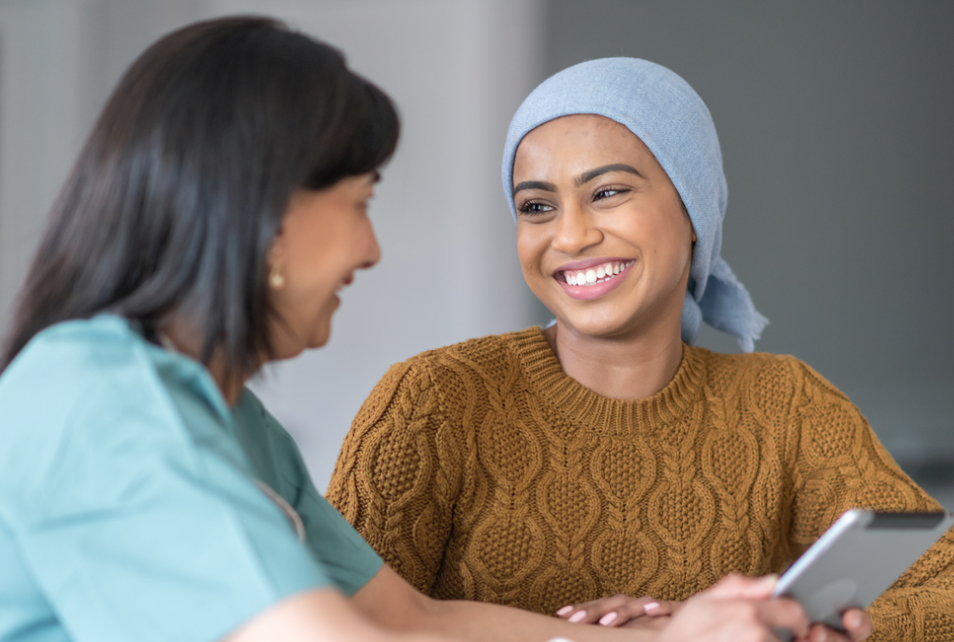
- Patient Care
- Leg relaxation massage
- Loin and leg relaxation massage
- Passive one-leg limit flexion and extension
- Passive single leg flexion and lateral pressure[maximum extent]
- Passive one leg flexion and extension
- Passively hold the knee to shake the waist
- Leg muscle relaxation massage
- Passive foot flexion and extension
- more(16)
- Health Library
- Cases & Stories
- The hope is within us|Revitalize life with therapy and loving care There is always light at the end of a tunnel
- Keep the “anus”, Keep Alive ---Ultra-low Rectal Cancer TEM Anus-preserving Surgery, Make Life More Dignified
- Local Recurrence and Metastasis after Gastric Cancer Surgery, Anastomotic Obstruction, and Weight Loss of 10kg in 3 Months are Solved with a Minor Surgery by Prof. Liu Haiying
- Medical Miracle! A Colon Cancer Patient with Multiple Metastases Who Was Assessed to Live Less Than Half a Year Has Survived for over 2 Years.
- Four Silk Banners on September 29! Guangzhou Royallee Cancer Center is Known as a Trusted Institution
- more(36)
- Interpreting hereditary gastrointestinal cancer genetic testing results
- HN Reliance Foundation Hospital collaborates with Dr Jatin P Shah of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center
- Congratulations to Our Immunization Champions, Seattle Public Schools Nurses and Stewart Lyman!
- Head and Neck Cancer: An emerging men’s health epidemic
- Speaking Up About Head and Neck Cancers
- more(13)
- About Us
Rehabilitation Training Videos
Cancer Treatment and Survivorship Cases
News & Views